News | August 17, 2016
Venus-like exoplanet might have oxygen atmosphere, but not life
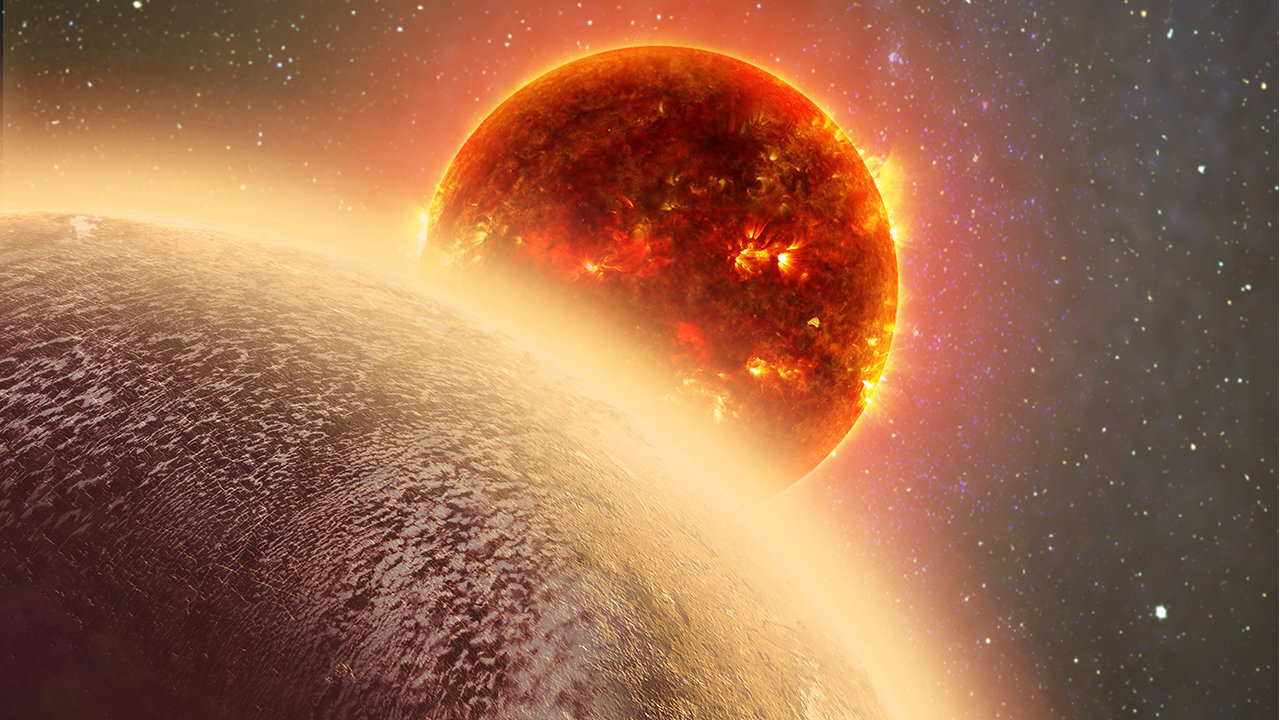

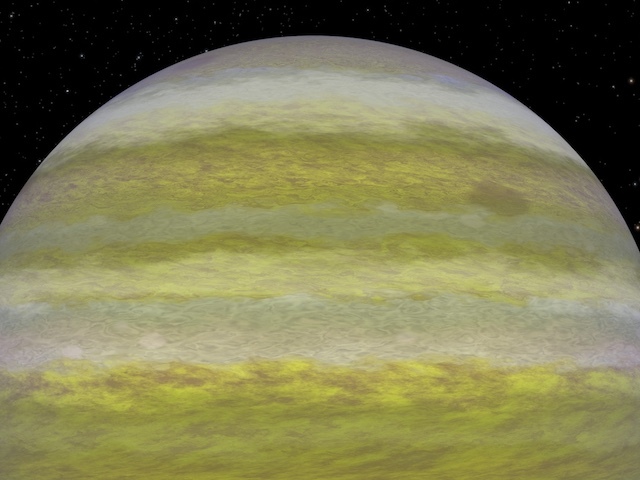
This artist's conception shows the rocky exoplanet GJ 1132b, located 39 light-years from Earth. New research shows that it might possess a thin, oxygen atmosphere - but no life due to its extreme heat. Credit: Dana Berry / Skyworks Digital / CfA
The distant planet GJ 1132b intrigued astronomers when it was discovered last year. Located just 39 light-years from Earth, it might have an atmosphere despite being baked to a temperature of around 450 degrees Fahrenheit. But would that atmosphere be thick and soupy or thin and wispy? New research suggests the latter is much more likely.
Harvard astronomer Laura Schaefer (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, or CfA) and her colleagues examined the question of what would happen to GJ 1132b over time if it began with a steamy, water-rich atmosphere.
Orbiting so close to its star, at a distance of just 1.4 million miles, the planet is flooded with ultraviolet or UV light. UV light breaks apart water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen, both of which then can be lost into space. However, since hydrogen is lighter it escapes more readily, while oxygen lingers behind.
"On cooler planets, oxygen could be a sign of alien life and habitability. But on a hot planet like GJ 1132b, it's a sign of the exact opposite - a planet that's being baked and sterilized," said Schaefer.
See also: ‘Electric wind’ can strip potential Earths of oceans, atmospheres
Since water vapor is a greenhouse gas, the planet would have a strong greenhouse effect, amplifying the star's already intense heat. As a result, its surface could stay molten for millions of years.
A "magma ocean" would interact with the atmosphere, absorbing some of the oxygen, but how much? Only about one-tenth, according to the model created by Schaefer and her colleagues. Most of the remaining 90 percent of leftover oxygen streams off into space, however some might linger.
"This planet might be the first time we detect oxygen on a rocky planet outside the solar system," said co-author Robin Wordsworth (Harvard Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences).
If any oxygen does still cling to GJ 1132b, next-generation telescopes like the Giant Magellan Telescope and James Webb Space Telescope may be able to detect and analyze it.
The magma ocean-atmosphere model could help scientists solve the puzzle of how Venus evolved over time. Venus probably began with Earthlike amounts of water, which would have been broken apart by sunlight. Yet it shows few signs of lingering oxygen. The missing oxygen problem continues to baffle astronomers.
Schaefer predicts that their model also will provide insights into other, similar exoplanets. For example, the system TRAPPIST-1 contains three planets that may lie in the habitable zone. Since they are cooler than GJ 1132b, they have a better chance of retaining an atmosphere.
This work has been accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal and is available online. The journal paper is authored by Laura Schaefer , Robin Wordsworth, Zachory Berta-Thompson (University of Colorado, Boulder), and Dimitar Sasselov (CfA).
Headquartered in Cambridge, Mass., the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA) is a joint collaboration between the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory and the Harvard College Observatory. CfA scientists, organized into six research divisions, study the origin, evolution and ultimate fate of the universe.
To read the paper, visit: